The spots and wrinkles on your face may be the result of UV rays you have been exposed to.
It is said that about 80% of skin aging such as spots, wrinkles, and sagging is "photoaging" caused by UV rays.
Once these spots and wrinkles appear, they are difficult to remove.
The most effective countermeasure is to prevent the formation of more spots and wrinkles.
The most effective way to prevent wrinkles and spots from forming is to prevent them from forming further, and to take good care of your skin every day so that the UV rays you are exposed to today will not turn into wrinkles and spots in the future.
Never give up and take good care of your skin, and you will have beautiful skin in the future.
What you may not know about UV rays
There are three types of ultraviolet rays: UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C. UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C are the most harmful to the skin.
UV-A and UV-B are the ones that affect the skin.
UV-C is absorbed by the ozone layer, so it hardly reaches the earth's surface.
UV-A: Most of the ultraviolet rays that reach the earth's surface are UV-A. It does not have a sudden effect on the skin, but it does affect it slowly and over time. UV-A is also known as the "aging ray.
UV-B: Although the amount of UV-B is small, a short exposure to UV-B can cause your skin to turn red or even black after a few days. UV-B is also known as the "sunburn ray.
Where are blemishes form
The skin is made up of the epidermis and dermis.
The epidermis is the one that is most closely related to blemishes.
The epidermis, which is about as thin as a piece of plastic wrap, is divided into four layers: the stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale.
The lowest layer, the stratum basale, contains melanocytes, which are factories that produce melanin. When exposed to ultraviolet rays, the melanocyte factories are ordered to produce melanin.
When exposed to ultraviolet rays, the melanocyte factory is ordered to produce melanin. The melanin produced by the melanocyte factory is passed on to the upper layers of the skin, thus protecting the important cell nuclei from ultraviolet rays.
This is an important role of melanin.
Normally, when melanin reaches the stratum corneum, it peels off from the surface through turnover.
However, when melanin is produced in excess for various reasons and the turnover cycle is disrupted, the melanin that should be removed gets stuck, resulting in pigmentation, or "spots.
The main cause of this is UV rays.
After years of exposure to UV rays, the melanocyte factory will continue to produce melanin in excess.
It also disrupts your skin's turnover, weakening its ability to expel melanin.
Some people's skin turns red when they get sunburned, and some people's skin turns black, but if your skin turns red quickly and then hardly turns black, you should be especially careful.
Your skin is susceptible to the effects of UV rays.
Other causes of blemishes include the overproduction of melanin by reactive oxygen species produced by smoking and stress, and delayed melanin elimination due to irregular lifestyle and poor blood circulation.
How to prevent blemishes?
The first step is to prevent UV rays.
In addition to spots caused by UV rays, freckles, melasma, and spots on acne and rash scars are also aggravated by UV rays.
UV rays are especially strong in spring and summer, but they basically fall all year round.
UV-A in particular can penetrate clouds and window glass, so even on cloudy days or when you are indoors, you need to take precautions.
Apply the right amount of sunscreen carefully and evenly.
Apply a layer of sunscreen to the T-zone, cheeks, and other areas prone to sunburn.
Be careful not to forget the areas behind your ears, décolleté and neck.
Even sunscreens with high SPF and PA values do not last all night if you apply it once in the morning. Reapply every two to three hours.
Use a parasol, hat, or sunglasses to keep UV rays away from your skin.
Use a sunscreen to protect your skin from UV rays.
Improve the barrier function of your skin.
When your skin is dry, its barrier function deteriorates, making it more susceptible to the effects of UV rays.
Make sure to moisturize your skin on a daily basis.
It is also important to follow a skin care regimen that promotes skin turnover for healthy, glowing skin.
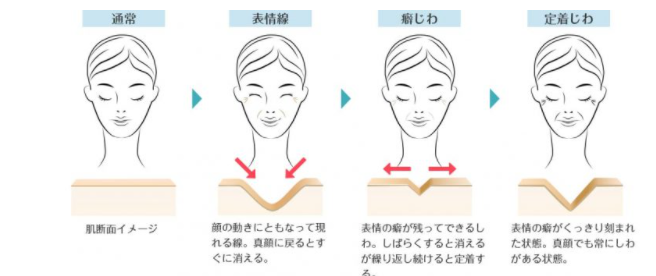
Where are Wrinkles Form
There are various causes of wrinkles, such as dry wrinkles caused by aging, loss of elasticity of the skin, aging wrinkles caused by loss of female hormone levels, dry wrinkles caused by cold and dry air, expression wrinkles caused by facial expressions, and UV wrinkles caused by damage from UV rays.
In particular, as the skin ages, it becomes less resistant to the effects of UV rays, which can cause skin cell aging.
Compared to aging wrinkles, UV wrinkles are characterized by hard and rough skin, and deep wrinkles.
How to prevent wrinkles
Daily moisturizing care is important for dry wrinkles. It is important to moisturize your skin daily to prevent fine lines from turning into large wrinkles.
Daily moisturizing care is also important for facial wrinkles. It is also important to moisturize your skin daily to prevent wrinkles from forming.
UV protection is also important for wrinkles.
It is important to use a combination of sunscreen and sun protection products to avoid exposure to UV rays.
When it comes to UV protection in skin care, Vitamin C!
Vitamin C is said to be an essential nutrient for beautiful skin. It promotes collagen production, inhibits melanin, and has an antioxidant effect, making it an excellent ingredient for UV protection.
However, vitamin C is unstable, easily oxidized, lacks penetrating power, and causes dryness when applied, making it difficult to use in cosmetics.
A new type of vitamin C derivative (ascorbyl palmitate 3Na phosphate) has been introduced to make up for these shortcomings.
A vitamin C derivative is an ingredient that is converted into vitamin C by an enzyme in the body, and has the same characteristics as vitamin C, but with improved penetration. Among these, the new vitamin C derivative has particularly high permeability, and because it contains palmitic acid, a lipid, it also has a moisturizing effect.
The new vitamin C derivative is expected to have a wide range of effects, from whitening to anti-aging (anti-wrinkle).
In addition, the new vitamin C derivative has a high synergistic effect, especially when combined with a water-soluble vitamin E derivative (sodium tocopheryl phosphate).
Water-soluble vitamin E is more permeable than conventional vitamin E, and is expected to prevent skin irritation, moisturize, retain moisture, and provide anti-inflammatory effects.
The combination of a new type of vitamin C derivative and a water-soluble vitamin E derivative, which has a variety of skin beautifying effects, is the perfect combination of ingredients for UV protection.
Freshness is the key to vitamin C
Although the new vitamin C derivative is more stable than conventional vitamin C, it is still fragile, and its effectiveness will gradually weaken if it is dissolved in liquid.
If you want to incorporate the new vitamin C derivative into your skin care regimen, we recommend that you use a product that is as fresh as possible, such as a two-part serum that you mix and use yourself, or a single-use, individually wrapped product, rather than a lotion containing the new vitamin C derivative.